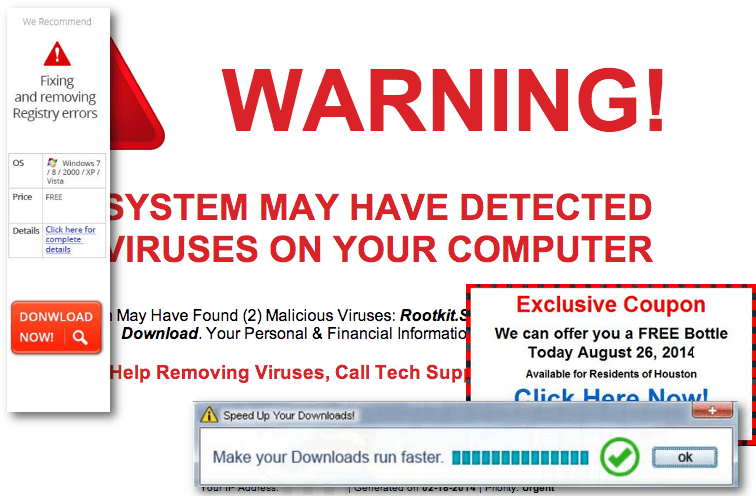
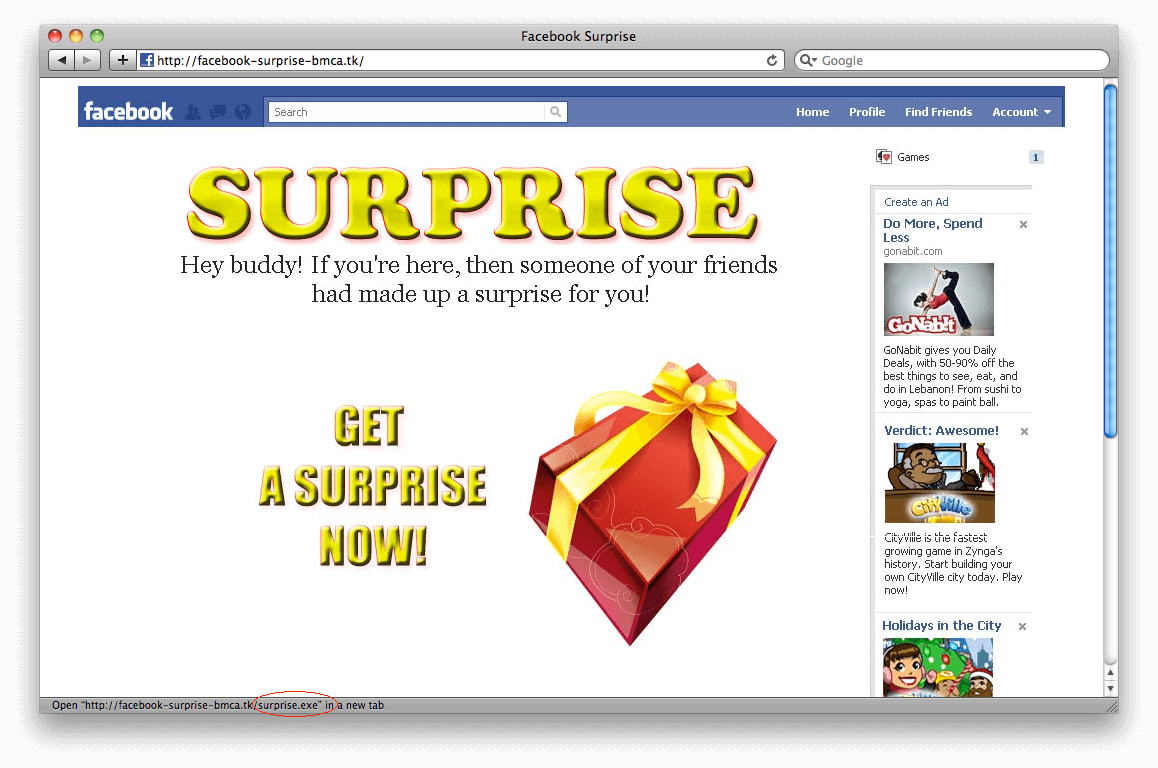
Cyber attack No. 1: Socially engineered malware
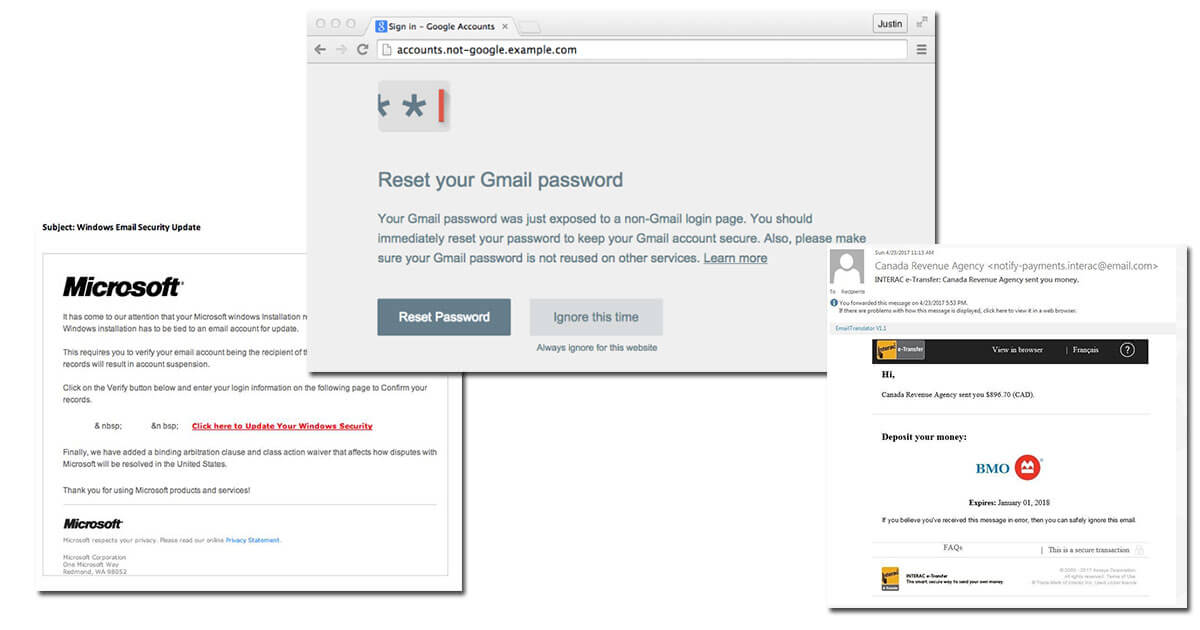
Cyber attack No. 2: Password phishing attacks
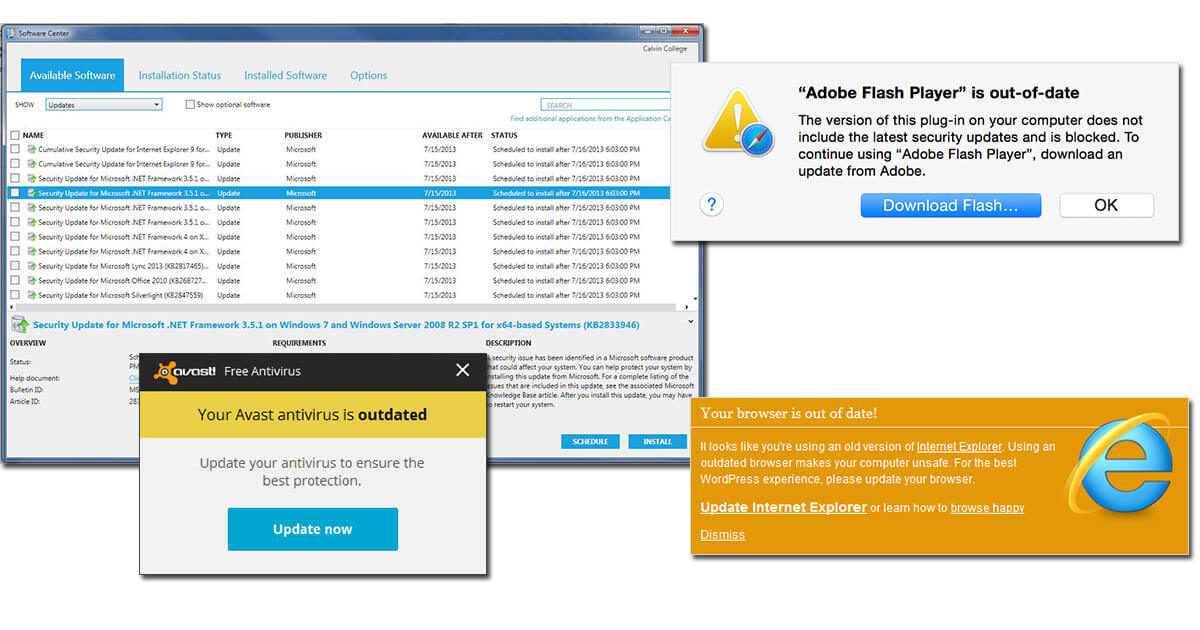
Cyber attack No. 3: Unpatched software
Cyber attack No. 4: Social media threats
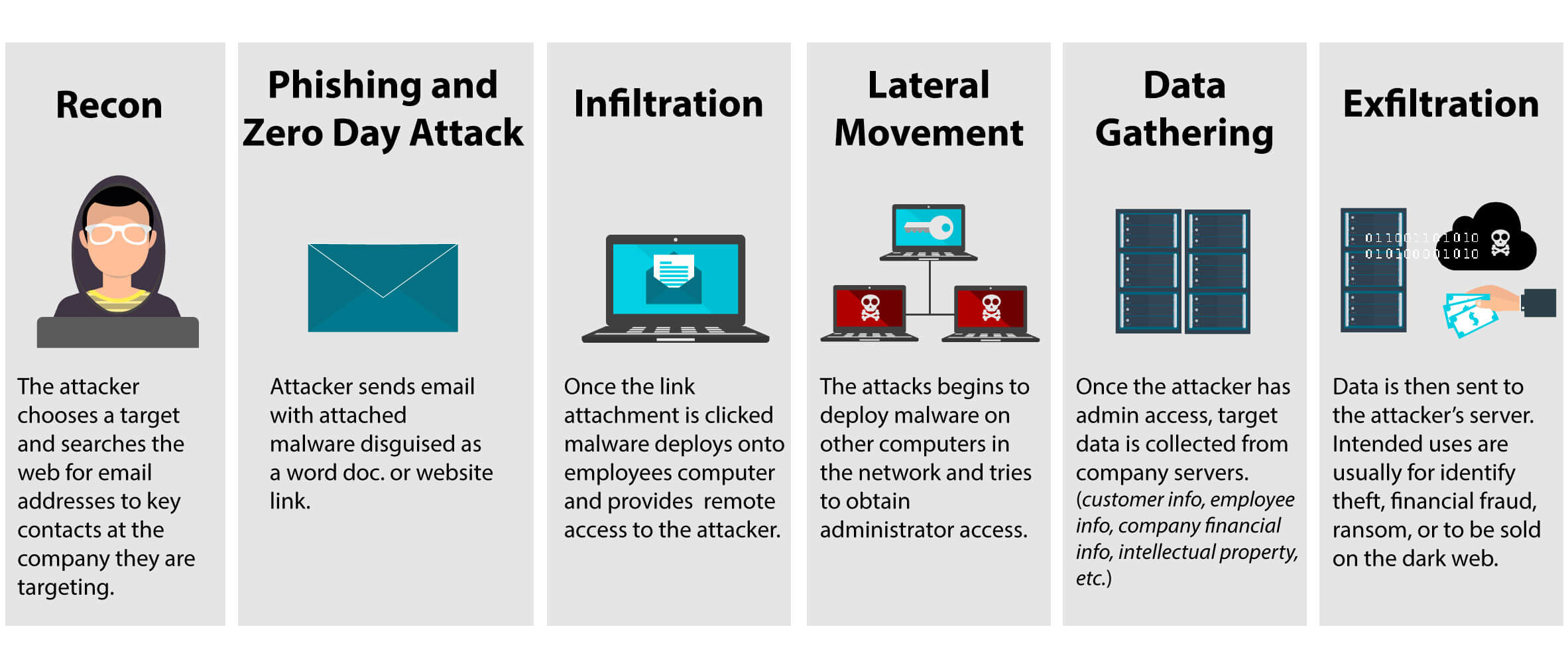
Cyber attack No. 5: Advanced persistent threats
Contact Us
If you're unsure how to identify your business’s top threats, and how to mitigate them, contact us at Netmon Services for a consultation where we can work with you to determine your business’s need for cybersecurity based on how you do business.